Reliable localization in a bioreactor
Fraunhofer ENAS is developing a new localization method based on magnetic fields. The inductive system allows reliable localization even in non-homogeneous and opaque substances. A first application is planned for localizing Sens-o-Spheres in bioreactors.

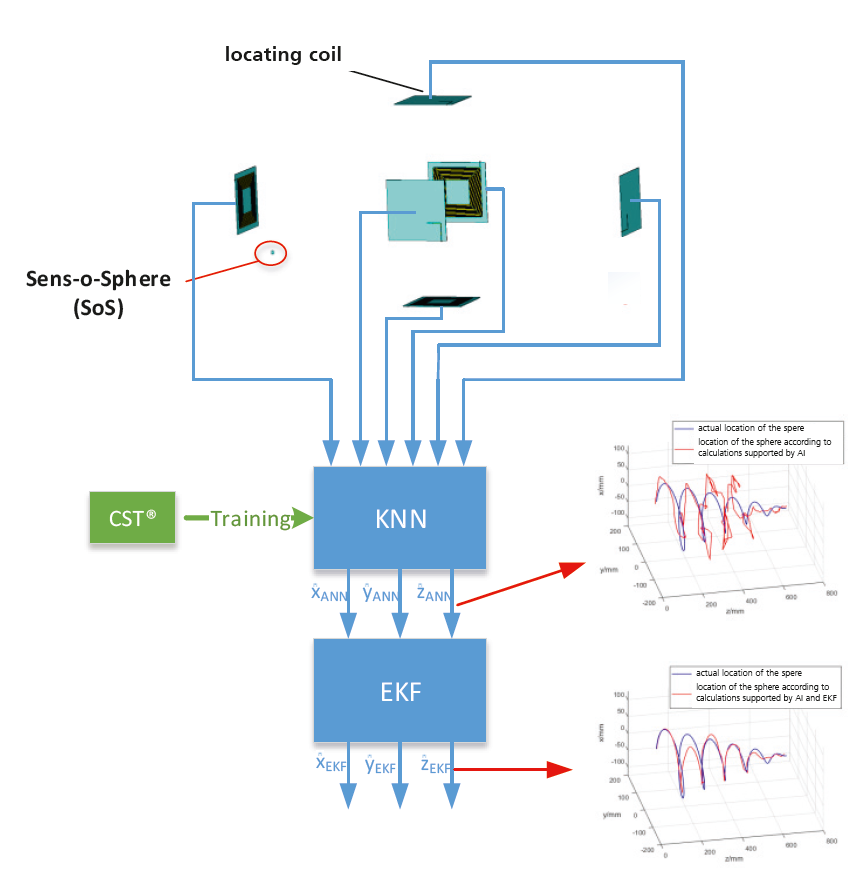
Sens-o-Spheres were developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Electronic Nano Systems ENAS in cooperation with TU Dresden and four industrial partners. The battery-operated, freely movable measuring probes are used for continuous monitoring of bioreactors. The measurements are transmitted wirelessly to a base station and evaluated there. Up to now, the spheres have been equipped with temperature sensors; in the future, they will also measure pH values and dissolved oxygen levels.
Measuring procedure
Inductive localization is particularly suitable for the use in bioreactors, where conventional locating technologies such as ultrasound or cameras have high error rates. An externally generated magnetic field induces electrical voltage on the charging coils of the Sens-o-Spheres. There, magnetic fields are generated, which are detected by locating coils. A neural network uses the signal strength to determine the position of the spheres. Equipped with a filter, the AI can take parasitic influences as well as the physical movements taking place in the reactor into account, thus producing reliable and accurate results.
Potential applications
In the future, inductive localization could also be used with RFID technologies, e.g., for centimeter-precise locating of labeled luggage in aircraft containers. In combination with other methods, high-precision localization applications in the areas of logistics, production and distribution are feasible.
Last modified: